Optimizing Urban Mobility with Smart Traffic Signals: Insights from Tampere, Finland

Study objectives and methodology
Our research aimed to assess the impact of different intersection control strategies based on indicators such as delays, stops, fuel consumption, and emissions under diverse traffic conditions. The study used the simulation software PTV VISSIM, expanded with the EnViVer Pro emissions module, we modeled two scenarios: a base scenario reflecting typical conditions and a stress test scenario with increased vehicle volumes from connecting side streets. Three traffic signal management approaches were evaluated in this field trial:
- Fixed-Time Control: Operates on a predefined schedule with no real-time responsiveness.
- Vehicle-Actuated Control: Adjusts signals based on vehicle detections, while still adhering to predetermined parameters.
- Adaptive Intersection Control by SWARCO: Continuously optimizes green times based on live traffic data, learning from traffic patterns and refining its decisions to maintain peak efficiency.
By simulating all six combinations (three control types across two traffic volumes), we measured their relative impacts on traffic flow and emissions.
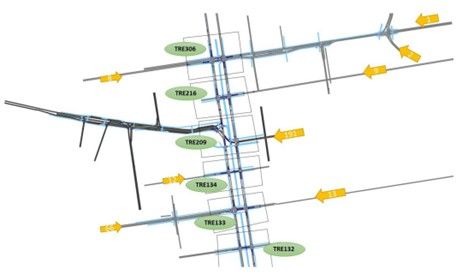
Figure 1 – Simulated intersections with feeding traffic from the side branches
What did we find out?
Our findings underscore the significant advantages of adaptive control over traditional systems, particularly in scenarios with high traffic volume. Under base traffic conditions, transitioning from fixed-time to vehicle-actuated control showed a 13% reduction in average delays. in the second set of scenarios with increased stress on the corridor, adaptive control halved average delays (50% reduction) and cut the average number of stops by 52% compared to fixed-time systems.
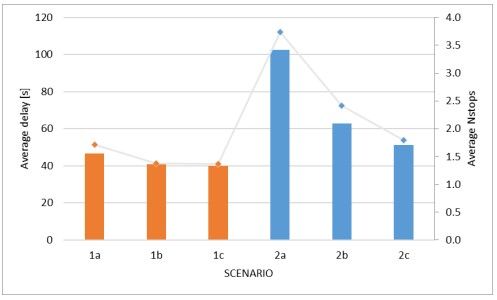
Figure 2 – Average delay (bars) and number of stops (points) for the six scenario compositions
What does it mean for the environment?
Fuel consumption trends closely followed the observed reductions in delays. While there isn’t a homogenous behaviour across intersections, in general, the peak in fuel consumption due to increased traffic shows reduction with the introduction of actuated and adaptive traffic light control systems. Notably, at intersections with the highest fuel consumption levels and the second set of scenarios with increased stress across the corridor, adaptive intersection control achieved substantial fuel savings.
Moreover, emissions of pollutants (volatile organic compounds (VOC), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and carbon monoxide (CO)) saw considerable declines along the corridor. At the most impacted intersections, with the introduction of adaptive intersection control, emissions reductions reached up to 44% compared to fixed-time operations, with visible benefits even in less congested scenarios.
Is there an impact on the Level of Service?
The Level of Service (LOS) indicator, reflecting traffic flow quality, exhibited overall improvements. The transition from fixed-time control to actuated and adaptive systems resulted in substantial reductions in delays, stops, and emissions, with the most significant improvements observed under higher traffic volumes.
Implications for the future
This study reinforces the potential of advanced adaptive traffic signal control systems to deliver substantial improvements in operational efficiency and environmental performance.
Because the study aims to investigate the impact of traffic signal control systems, the assessment is carried out in an isolated environment, excluding other closely connected factors such as induced demand or modal shift. The study's results must be read with a crucial note that such technologies offer significant potential, especially when coupled with aligned policies.
As cities strive to achieve sustainability goals and alleviate congestion, intelligent traffic management technologies like adaptive signal control stand out as pivotal solutions. By minimizing delays, reducing fuel consumption, and lowering emissions, these technologies not only enhance urban mobility but also contribute significantly to cleaner air and climate action.
The numbers speak for themselves. Don't hesitate to get in touch with us and embrace the future with SWARCO - The Better Way. Every Day.
If you want to know more about the study, find the full report here.
Important note
Because the study aims to investigate the impact of traffic signal control systems, the assessment is carried out in an isolated environment, excluding other closely connected factors such as induced demand or modal shift. The study's results must be read with a crucial note that such technologies offer significant potential, especially when coupled with aligned policies.